Coronavirus far more likely than Sars to bond to human cells due to HIV-like mutation, scientists say
- Research by team from Nankai University shows new virus has mutated gene similar to those found in HIV and Ebola
- Finding may help scientists understand how the infection spreads and where it came from
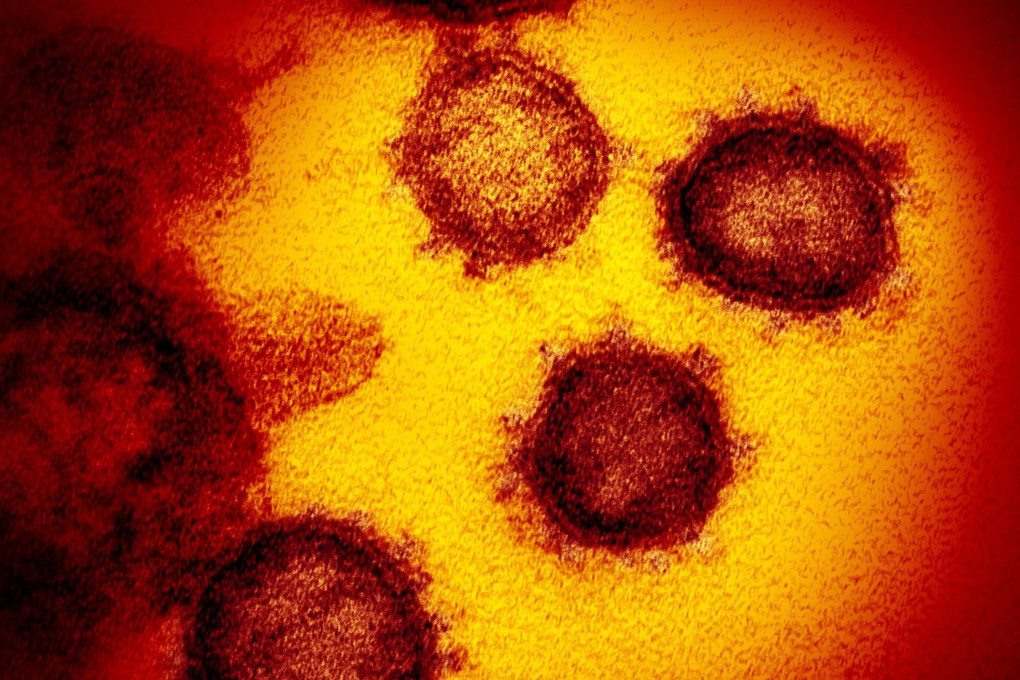
The discovery could help to explain not only how the infection has spread but also where it came from and how best to fight it.
Scientists showed that Sars (severe acute respiratory syndrome) entered the human body by binding with a receptor protein called ACE2 on a cell membrane. And some early studies suggested that the new coronavirus, which shares about 80 per cent of the genetic structure of Sars, might follow a similar path.
But the ACE2 protein does not exist in large quantities in healthy people, and this partly helped to limit the scale of the Sars outbreak of 2002-03, in which infected about 8,000 people around the world.
Other highly contagious viruses, including HIV and Ebola, target an enzyme called furin, which works as a protein activator in the human body. Many proteins are inactive or dormant when they are produced and have to be “cut” at specific points to activate their various functions.
When looking at the genome sequence of the new coronavirus, Professor Ruan Jishou and his team at Nankai University in Tianjin found a section of mutated genes that did not exist in Sars, but were similar to those found in HIV and Ebola.